“Many investors are bracing for further turbulence in the stock market in coming weeks, with few expectations that the dramatic swings will subside soon, given uncertainty over the economic and interest-rate outlooks. ‘The market is vulnerable right now,’ said Terri Spath, chief investment officer of Sierra Investment Management. ‘A number of technical indicators have broken down, making it hard to call for any sort of bottom.”
Wursthorn, Michael. Wall Street Journal, Eastern edition; New York, N.Y. 03 Jan 2019: B.1
Investors Rush to Buy Up Stocks — As rally powers major indexes toward record, traders are wary of missing out on gains
Ramkumar, Amrith. Headline, Wall Street Journal, Eastern edition; New York, N.Y. 01 Apr 2019: A.1.
“There is a large academic literature on whether market returns are predictable. The general conclusion is that it is impossible to predict the market return with any confidence… ‘A Comprehensive Look at the Empirical Performance of Equity Premium Prediction,’ by Amit Goyal and Ivo Welch (Review of Financial Studies, 2008), is a good summary of the evidence.”
Kenneth French, Roth Family Distinguished Professor of Finance
Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth College
Market Review
As you can see by the first 2 quotes above, the newspapers and so called “experts” are not really good at predicting the future, and investors should not rely on what they read in the newspapers for investing in the market. The quotes also show how “sentiment” can change quickly in the press. Investors should heed the advice in the 3d quote above, as it is impossible to predict the future persistently and consistently.
Below are the indices we follow.
| Periodic Performance; % | ||||||
| By 03/2019; Default Currency: USD | ||||||
| 3 Months | 6 Months | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years | |
| S&P 500 | 13.65 | -1.72 | 9.50 | 13.51 | 10.91 | 15.92 |
| Russell 2000 | 14.58 | -8.56 | 2.05 | 12.92 | 7.05 | 15.36 |
| Russell 2000 Value | 11.93 | -8.97 | 0.17 | 10.86 | 5.59 | 14.12 |
| MSCI World ex US (net div.) | 10.45 | -3.67 | -3.14 | 7.29 | 2.20 | 8.82 |
| MSCI World ex US Small Cap (net div.) | 10.93 | -7.00 | -8.66 | 7.28 | 3.69 | 12.25 |
| MSCI Emerging Markets (net div.) | 9.92 | 1.71 | -7.41 | 10.68 | 3.68 | 8.94 |
| Bloomberg Barclays U.S. T Bond | 1.23 | 3.00 | 3.17 | 0.95 | 1.26 | 1.45 |
| ICE BofAML 1-Year US T Note | 0.82 | 1.61 | 2.44 | 1.21 | 0.85 | 0.70 |
Obviously it was a very good quarter. One of the best in several decades. The S&P 500 gained 13.65%, and the Russell 2000 (small cap) was up 14.58%. The leadership of growth stocks has come to the forefront so far in 2019 compared to value stocks. Growth stocks, as measured by the Russell 1000 Growth Index, advanced 2.85% for the month and 16.10% for the quarter, while value stocks, as measured by the Russell 1000 Value Index, gained 0.64% and 11.93%, respectively, in March and in Q1.
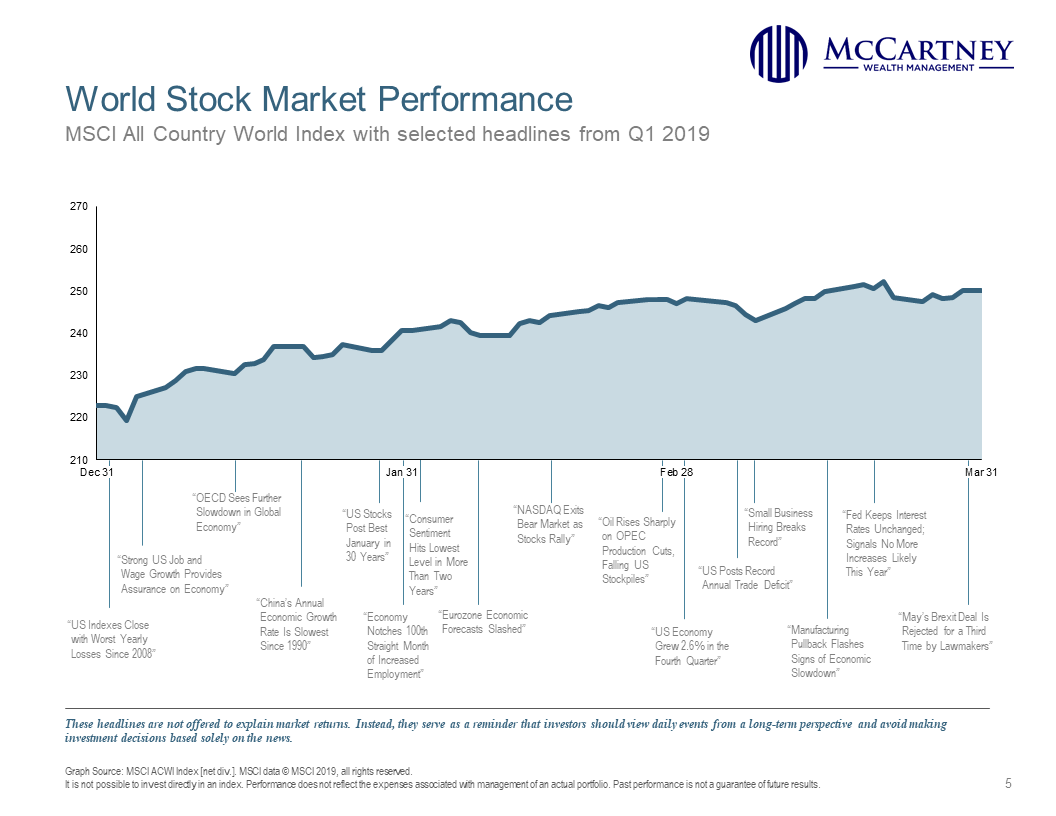
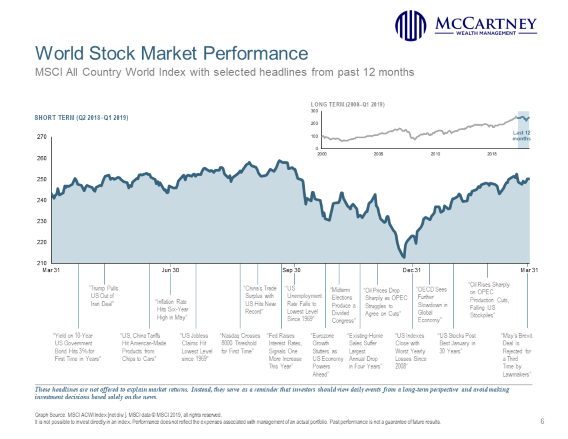
International equities started the year off strong as well, but their gains have not been as good as U.S. equity markets. The MSCI World ex USA Index, a broad measure of international equities, gained 10.45% for the quarter, and Emerging Markets were up 9.92%. Below are graphics of the MSCI All World Country Index for the last quarter and year. It gives a pretty good picture of how world equity markets have performed, with corresponding news headlines throughout the timeline.
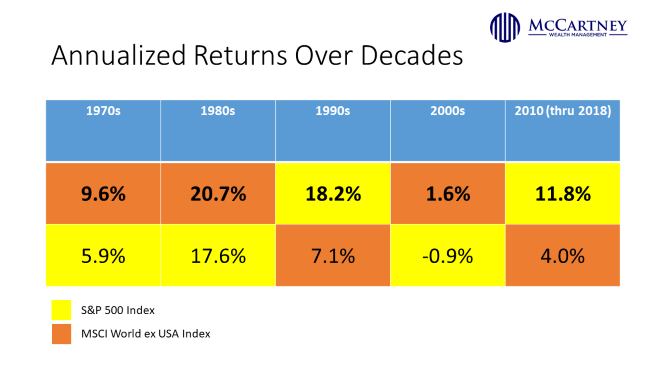
However, it is important to note that since 1970, international stocks outperformed US stocks in the decades of the 70’s, 80’s, and 2000’s, or 3 of the last 5 decades. There is a benefit to long-term diversification.
Below is a very good piece from our friends at Dimensional talking about long-term discipline in investing. Too many people make bad decisions based upon the short term. Variability in returns is very high in the short term, as evidenced by the 4th quarter of last year compared to the 1st quarter of this year. I feel sorry for Sierra Investment Management’s clients referenced in the very first quote at the beginning, whoever they may be. As evidenced by the quote from the Wall Street Journal on January 3, 2019, if their clients followed Sierra’s advice, they would have missed one of the best quarters in several decades.
Déjà Vu All Over Again
Dimensional Fund Advisors
Investment fads are nothing new. When selecting strategies for their portfolios, investors are often tempted to seek out the latest and greatest investment opportunities. Over the years, these approaches have sought to capitalize on developments such as the perceived relative strength of particular geographic regions, technological changes in the economy, or the popularity of different natural resources. But long-term investors should be aware that letting short term trends influence their investment approach may be counterproductive. As Nobel laureate Eugene Fama said, “There’s one robust new idea in finance that has investment implications maybe every 10 or 15 years, but there’s a marketing idea every week.”
WHAT’S HOT BECOMES WHAT’S NOT
Looking back at some investment fads over recent decades can illustrate how often trendy investment themes come and go. In the early 1990s, attention turned to the rising “Asian Tigers” of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. A decade later, much was written about the emergence of the “BRIC” countries of Brazil, Russia, India, and China and their new place in global markets. Similarly, funds targeting hot industries or trends have come into and fallen out of vogue. In the 1950s, the “Nifty Fifty” were all the rage. In the 1960s, “go‑go” stocks and funds piqued investor interest. Later in the 20th century, growing belief in the emergence of a “new economy” led to the creation of funds poised to make the most of the rising importance of information technology and telecommunication services. During the 2000s, 130/30 funds, which used leverage to sell short certain stocks while going long others, became increasingly popular. In the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, “Black Swan” funds, “tail-risk-hedging” strategies, and “liquid alternatives” abounded. As investors reached for yield in a low interest rate environment in the following years, other funds sprang up that claimed to offer increased income generation, and new strategies like unconstrained bond funds proliferated. More recently, strategies focused on peer-to-peer lending, cryptocurrencies, and even cannabis cultivation and private space exploration have become more fashionable. In this environment, so-called “FAANG” stocks and concentrated exchange-traded funds with catchy ticker symbols have also garnered attention among investors.
THE FUND GRAVEYARD
Unsurprisingly, however, numerous funds across the investment landscape were launched over the years only to subsequently close and fade from investor memory. While economic, demographic, technological, and environmental trends shape the world we live in, public markets aggregate a vast amount of dispersed information and drive it into security prices. Any individual trying to outguess the market by constantly trading in and out of what’s hot is competing against the extraordinary collective wisdom of millions of buyers and sellers around the world.
With the benefit of hindsight, it is easy to point out the fortune one could have amassed by making the right call on a specific industry, region, or individual security over a specific period. While these anecdotes can be entertaining, there is a wealth of compelling evidence that highlights the futility of attempting to identify mispricing in advance and profit from it.
It is important to remember that many investing fads, and indeed, most mutual funds, do not stand the test of time. A large proportion of funds fail to survive over the longer term. Of the 1,622 fixed income mutual funds in existence at the beginning of 2004, only 55% still existed at the end of 2018. Similarly, among equity mutual funds, only 51% of the 2,786 funds available to US-based investors at the beginning of 2004 endured.1
WHAT AM I REALLY GETTING?
When confronted with choices about whether to add additional types of assets or strategies to a portfolio, it may be helpful to ask the following questions:
- What is this strategy claiming to provide that is not already in my portfolio?
- If it is not in my portfolio, can I reasonably expect that including it or focusing on it will increase expected returns, reduce expected volatility, or help me achieve my investment goal?
- Am I comfortable with the range of potential outcomes?
If investors are left with doubts after asking any of these questions, it may be wise to use caution before proceeding. Within equities, for example, a market portfolio offers the benefit of exposure to thousands of companies doing business around the world and broad diversification across industries, sectors, and countries. While there can be good reasons to deviate from a market portfolio, investors should understand the potential benefits and risks of doing so.
In addition, there is no shortage of things investors can do to help contribute to a better investment experience. Working closely with a financial advisor can help individual investors create a plan that fits their needs and risk tolerance. Pursuing a globally diversified approach; managing expenses, turnover, and taxes; and staying disciplined through market volatility can help improve investors’ chances of achieving their long-term financial goals.
CONCLUSION
Fashionable investment approaches will come and go, but investors should remember that a long-term, disciplined investment approach based on robust research and implementation may be the most reliable path to success in the global capital markets.
A Few Other Interesting Articles From the Last Quarter (Click on Links Below)
Analyst Forecasts – A Lesson in Futility
Investing for Retirement Isn’t Just About Money
Key Questions for Long-Term Investors
Until next time,
Mike and Emily